Built-in CAN bus in GPS trackers: a new trend in advanced telematics hardware
GPS tracker manufacturers are driving product innovation more than ever before, implementing modern built-in modules directly into GPS trackers capable of accessing much richer vehicle data streams for a wider range of analytics data about fleets. One such built-in module includes increased capability with CAN (Controller Area Network) support.
Hardware manufacturers are improving their GPS trackers by implementing built-in CAN modules. There are two ways to access the telematics data directly from the vehicle: CAN and OBDII. CAN-bus transmits more parameters because it connects directly to the vehicle's data stream and provides more useful telemetry data.
This technology is being embraced by businesses that need advanced fleet management solutions but also want options that are easier to implement due to straightforward installation and monitoring processes compared to other options such as OBDII which yields more limited parameters.
Built-in CAN bus vs. separate CAN adapter
The advantages of using GPS trackers with built-in CAN adapters as opposed to separate and external devices are immense. The size and design of GPS hardware are important considerations for designers and manufacturers, especially when it comes to incorporating new features into a product. A great way to reduce size without sacrificing functionality is by using a built-in CAN adapter.
This type of hardware requires less effort for installation than other CAN reading devices, as the GPS tracker and CAN adapter are housed in one device. Additionally, since only one device is used rather than two, fewer wires need to be connected.
Since the CAN reader is integrated into the GPS tracker, it eliminates the need for additional monitoring and support of a second device. This makes it easier for businesses to track location and performance data in real-time with minimal setup time and cost associated with extra equipment.
In comparing GPS trackers with built-in CAN and OBDII models, we find that CAN-based devices transmit more telematics data that can be used for complicated and detailed fleet management scenarios, whereas OBDII trackers transmit less actionable data but have a more convenient Plug and Play installation process. So, you will have to determine for yourself which is the better tradeoff: more telemetry data or ease of installation.
Adoption of built-in CAN by Teltonika Telematics and Queclink
Teltonika Telematics and Queclink are leading manufacturers of GPS trackers for fleet monitoring. They always strive to deliver the highest quality products in telematics, with a commitment to cutting-edge technology and innovation. Both of these manufacturers are incorporating built-in modules such as CAN adapters into their GPS hardware as described above, setting a higher standard for the industry. These brands are committed to expanding connectivity by providing more functionality and use cases than ever before.
Teltonika offers two series and one separate model with built-in CAN adapters – the FMx150 series and FMBx40 series, and the FMC650 model. The FMC650 is designed for professional applications and supports a tachograph. Furthermore, both the FMx150 and FMC650 models work on CAT 1 and CAT M1 networks with 2G fallback, whereas the FMBx40 series only supports 2G. All models support Bluetooth, 1-wire, and digital and analog inputs, which allow for the connection of many devices to collect additional telemetry.
Queclink offers two models with built-in CAN adapters – the GV350CEU and GV355CEU. The GV350CEU has the capability to read data from BLE, fuel, and 1-wire sensors, as well as monitor driver behavior using its built-in accelerometer. Meanwhile, the GV355CEU is a more advanced model that supports a tachograph. Both Queclink devices operate on CAT 1 networks with 2G fallback.
Business applications of CAN bus data
Using CAN bus parameters is highly beneficial when fleet monitoring is a crucial part of your business. GPS trackers equipped with CAN interfaces can help solve various operational problems, as explored below.
Fleet maintenance
CAN-compatible devices transmit multiple vital vehicle parameters that better allow mechanics and service personnel to extend the life of corporate fleets through preventative maintenance. These devices read and transmit data such as:
- Check engine indicator status
- Coolant and engine oil temperature
- Distance traveled with check engine indicator triggered
These parameters can all be monitored on a single platform, enabling efficient control over the fleet's health. Early detection of out-of-parameter readings allows for the scheduling of crucial vehicle maintenance tasks to prevent losses of operational assets.
Risk management and safety control
Devices that come with built-in CAN interfaces support fleet managers and dispatchers when monitoring various safety parameters to mitigate multiple risks for businesses like:
- Seat belt status
- Low tire pressure
- ABS status
Creating events based on specific parameters can significantly improve safety management. Additionally, safety control parameters can prevent unnecessary expenses such as fines or tickets for not wearing a seatbelt.
Electric vehicles telematics
As the popularity of electric vehicles grows, the number of available parameters transmitted via CAN-bus is also increasing. In EVs, several additional parameters can be monitored:
- Charging status
- Battery level
- Battery temperature
Obtaining these parameters through the CAN bus is important for electric vehicles, as they provide valuable insights that can keep these vehicles on the road. Incorporating new parameters is a significant step that enhances the ability to remotely monitor EVs
Managing CAN bus parameters in Navixy
The use of GPS trackers with CAN support is on the rise in the Navixy platform due to their ease of installation and monitoring capabilities. This hardware promises to revolutionize GPS monitoring of vehicles, and Navixy is leading the way in incorporating these devices into everyday fleet management scenarios.
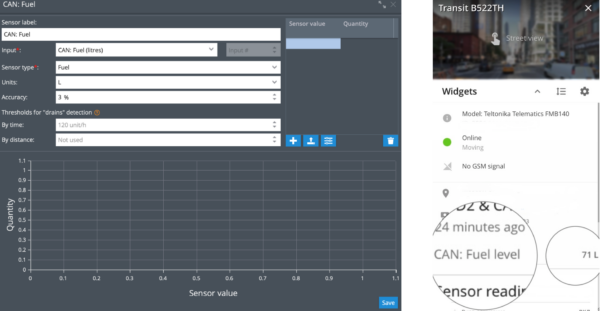
Navixy offers a convenient and functional platform interface for creating, editing, and managing telematics data parameters based on CAN telemetry. We also provide you the ability to create “virtual sensors” based on any CAN parameter received from your GPS hardware. As soon as the sensor is created, the corresponding value will be displayed when the data is received.
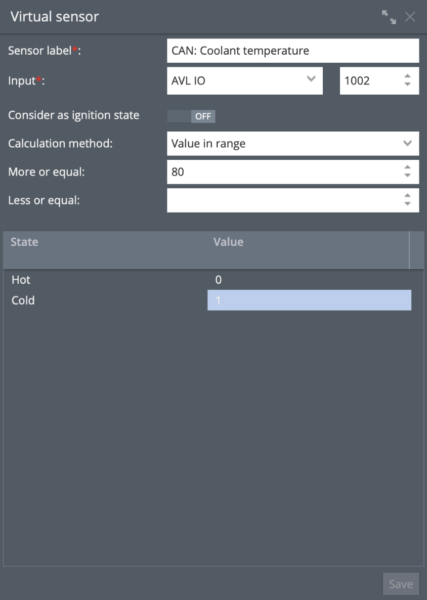
Additionally, the new "Virtual Sensor" capability provides other advanced functions such as calibration tables, sensors based on specific bits, and assigning text for specific values, which allows you to receive results as text instead of just numerical values. For example, you could assign the text "hot" for high coolant values and "cold" for low ones—messages far more readily understood than plain numbers.
Navixy channel partners have the flexibility to create their own applications and utilize CAN parameters according to their preferences using the Navixy API. A dedicated API call and helpful guide are available to assist with complex tasks and custom solution development.
With all this functionality, Navixy is able to offer user-friendly visualization for CAN parameters and advanced tools for sophisticated and complex telematics use cases. Feel free to reach out to our team of experts at [email protected] to find out more.